3D Printing at Home
What is a 3D Printer?
Thanks to the process of 3D Printing, the concept of downloading and printing a pair of shoes may not be all that far-fetched.
3D Printing is the process of taking a 3 dimensional digital computer model, and turning it in to a solid, real life object that you can hold in your hands.
A 3D printer is works similar to a regular ink based printer, but instead of using ink it uses materials such as ceramic, metal and plastic to build up an object.
History of 3D Printers
3D Printing is not a new technology and has been around since the early 1980’s. Back then however, 3D Printers were quite costly and could range anywhere between $30,000 to $100,000 each. This of course meant that their use was usually restricted to concept designs and usually confined to laboratories.
Now days an entry level 3D Printer can be purchased for around $600 and even less if the printer is built from a kit. At these prices the marketplace for 3D printing user base has been expanded up to individuals.
Preparing a 3D Print
The process of performing a 3D print starts with the computer model. This model can be designed using any number of professional 3d software tools, such as AutoCAD, Poser or Realsoft 3d but they do come at a price. There are also many free alternatives such as Google Sketchup or Seamless3d which could also do the job.
This model is then ‘sliced’ into very fine horizontal layers by a piece of software known as slicing software. Some examples of slicing software include Slic3r and Skeinforge. The printer then builds up the object by creating these layers, one at a time with the material until the object is built.
Methods of 3D Printing
There are many different methods for creating a 3D printed layer depending on the material and type of 3D printer that is being used.
The most common method is known as Fused Deposition Modelling or FDM. With this method, a spool of plastic filament is used as the material and is fed into the printer.
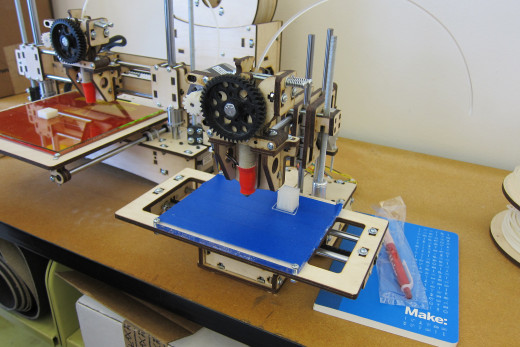
The Process of 3D Printing
As the filament is unwound and fed into the printer’s nozzle, which is known as the hotend. The hotend is heated up to where the filament is at melting point (which is anywhere between 170-240 degrees Celsius). The printer then proceeds to draw the horizontal layer onto the print bed with the hotend.
In a ‘reprap’ (one of the most common 3D printers on the market), a series of stepper motors are used to drive the X, Y and Z positioning of the hotend by use of both belt pulleys and threaded rods. Because of their quick, lightweight movement, belt pulleys are often used for the X and Y motion, while a threaded rods are used to drive the Z axis because of their slow but strong movements (they have to move a lot more than just the hotend). A stepper motor is a type of motor that can be very accurately controlled using a circuit known as a controller. A reprap will generally utilize 5 stepper motors- one for the horizontal left and right movement (X), one for the horizontal back and forward movement (Y), one for driving filament into the hotend, and two for the vertical movement of either the hotend of the print bed.
The print bed is often heated so as to ensure that the initial layers of the print stick to the surface without warping. It is an optional component of a 3D printer however it is definitely recommended.
Once the layer is done the print bed moves down and the next layer is drawn on top of the previous. Alternatively (depending on the type of printer being used), the hotend could move up as opposed to the bed moving down. The melted plastic is quick to set which means that the layers can defy gravity slightly and print (to some degree) layers which do not require a direct/complete layer below it. This process continues until the 3D object is done.
Conclusion
I hope that this has given you a greater understanding of what a 3D printer is and how they work.
It is a concept that is gaining a fast popularity and reputation and is becoming more and more obtainable to households than ever before.
It is still unclear as to the impact of what 3D printing will have on different industries, but I am sure we are likely to see a massive change to the way we work and live in our everyday lives in the not to distant future.
- How to Build a 3D Printer on a Budget
Here are some tips that I found saved me a little bit of money when building my rerap. - 6 Great Tools for your 3D Printer
A few handy tools I keep close at hand when working on my repap printer. Some of these things may sound like a no-brainier, others are handy tips for things you may have lying around your workshop - How NOT to Build a 3d Printer
Join me on my 24 month journey of how to make every possible mistake when building your own 3d printer